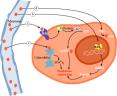
 Melatonin is a neurohormone synthesized and secreted at night by the pineal gland, which is located inside the brain.
Melatonin is a neurohormone synthesized and secreted at night by the pineal gland, which is located inside the brain.One of the most important properties of melatonin is its antitumoral action besides its antioxidative and sleep-inducing effects. The melatonin levels in the body play an important role in the immune system activity, specifically the one mediated by cells, in which the interleukins regulate the immune response. It is well documented that melatonin is able to activate the production of IL-2 which constitutes the main antitumoral cytokine in humans. It also stimulates the production of interferon by T cells, and IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, nitric oxide and other reactive oxygen species by monocytes.
Low levels of melatonin have been associated with an increased risk of several diseases, including cancer and other chronic degenerative diseases. Melatonin plays an important role in the survival and quality of life of cancer patients. Clinical studies have reported significantly less adverse effects during chemo and radiotherapy after melatonin administration. The dose of melatonin used in the studies were 10-50 milligrams per day.
The Oasis of Hope Hospital ozonized AHT and UV blood irradiation in combination with prescribed melatonin appears to promote the production and antitumoral action of IL-2.
The Oasis of Hope Hospital


No comments:
Post a Comment